ryu/lib.rs
1//! [![github]](https://github.com/dtolnay/ryu) [![crates-io]](https://crates.io/crates/ryu) [![docs-rs]](https://docs.rs/ryu)
2//!
3//! [github]: https://img.shields.io/badge/github-8da0cb?style=for-the-badge&labelColor=555555&logo=github
4//! [crates-io]: https://img.shields.io/badge/crates.io-fc8d62?style=for-the-badge&labelColor=555555&logo=rust
5//! [docs-rs]: https://img.shields.io/badge/docs.rs-66c2a5?style=for-the-badge&labelColor=555555&logo=docs.rs
6//!
7//! <br>
8//!
9//! Pure Rust implementation of Ryū, an algorithm to quickly convert floating
10//! point numbers to decimal strings.
11//!
12//! The PLDI'18 paper [*Ryū: fast float-to-string conversion*][paper] by Ulf
13//! Adams includes a complete correctness proof of the algorithm. The paper is
14//! available under the creative commons CC-BY-SA license.
15//!
16//! This Rust implementation is a line-by-line port of Ulf Adams' implementation
17//! in C, [https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu][upstream].
18//!
19//! [paper]: https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3192369
20//! [upstream]: https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu
21//!
22//! # Example
23//!
24//! ```
25//! fn main() {
26//! let mut buffer = ryu::Buffer::new();
27//! let printed = buffer.format(1.234);
28//! assert_eq!(printed, "1.234");
29//! }
30//! ```
31//!
32//! ## Performance
33//!
34//! The [dtoa-benchmark] compares this library and other Rust floating point
35//! formatting implementations across a range of precisions. The vertical axis
36//! in this chart shows nanoseconds taken by a single execution of
37//! `ryu::Buffer::new().format_finite(value)` so a lower result indicates a
38//! faster library.
39//!
40//! [dtoa-benchmark]: https://github.com/dtolnay/dtoa-benchmark
41//!
42//! 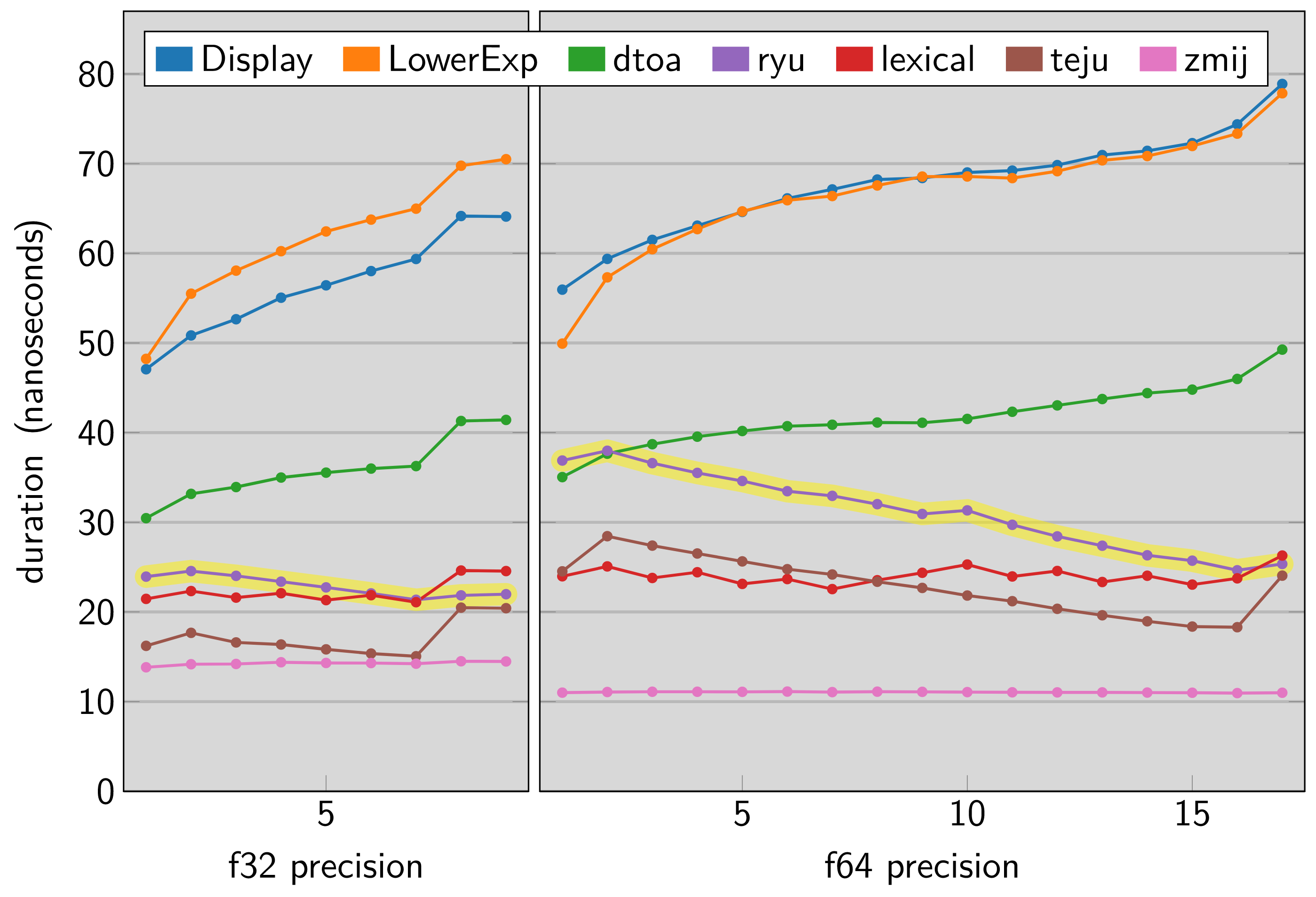
43//!
44//! You can run upstream's benchmarks with:
45//!
46//! ```console
47//! $ git clone https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu c-ryu
48//! $ cd c-ryu
49//! $ bazel run -c opt //ryu/benchmark
50//! ```
51//!
52//! And the same benchmark against our implementation with:
53//!
54//! ```console
55//! $ git clone https://github.com/dtolnay/ryu rust-ryu
56//! $ cd rust-ryu
57//! $ cargo run --example upstream_benchmark --release
58//! ```
59//!
60//! These benchmarks measure the average time to print a 32-bit float and average
61//! time to print a 64-bit float, where the inputs are distributed as uniform random
62//! bit patterns 32 and 64 bits wide.
63//!
64//! The upstream C code, the unsafe direct Rust port, and the safe pretty Rust API
65//! all perform the same, taking around 21 nanoseconds to format a 32-bit float and
66//! 31 nanoseconds to format a 64-bit float.
67//!
68//! There is also a Rust-specific benchmark comparing this implementation to the
69//! standard library which you can run with:
70//!
71//! ```console
72//! $ cargo bench
73//! ```
74//!
75//! The benchmark shows Ryū approximately 2-5x faster than the standard library
76//! across a range of f32 and f64 inputs. Measurements are in nanoseconds per
77//! iteration; smaller is better.
78//!
79//! ## Formatting
80//!
81//! This library tends to produce more human-readable output than the standard
82//! library's to\_string, which never uses scientific notation. Here are two
83//! examples:
84//!
85//! - *ryu:* 1.23e40, *std:* 12300000000000000000000000000000000000000
86//! - *ryu:* 1.23e-40, *std:* 0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000123
87//!
88//! Both libraries print short decimals such as 0.0000123 without scientific
89//! notation.
90
91#![no_std]
92#![doc(html_root_url = "https://docs.rs/ryu/1.0.22")]
93#![allow(
94 clippy::cast_lossless,
95 clippy::cast_possible_truncation,
96 clippy::cast_possible_wrap,
97 clippy::cast_sign_loss,
98 clippy::checked_conversions,
99 clippy::doc_markdown,
100 clippy::expl_impl_clone_on_copy,
101 clippy::if_not_else,
102 clippy::many_single_char_names,
103 clippy::missing_panics_doc,
104 clippy::module_name_repetitions,
105 clippy::must_use_candidate,
106 clippy::needless_doctest_main,
107 clippy::similar_names,
108 clippy::too_many_lines,
109 clippy::unreadable_literal,
110 clippy::unseparated_literal_suffix,
111 clippy::wildcard_imports
112)]
113
114mod buffer;
115mod common;
116mod d2s;
117#[cfg(not(feature = "small"))]
118mod d2s_full_table;
119mod d2s_intrinsics;
120#[cfg(feature = "small")]
121mod d2s_small_table;
122mod digit_table;
123mod f2s;
124mod f2s_intrinsics;
125mod pretty;
126#[cfg(test)]
127mod tests;
128
129pub use crate::buffer::{Buffer, Float};
130
131/// Unsafe functions that mirror the API of the C implementation of Ryū.
132pub mod raw {
133 pub use crate::pretty::{format32, format64};
134}